Ergothioneine has become one of the most discussed antioxidant compounds in the field of cellular health and longevity research. Although it was first discovered more than a century ago, only in recent decades have scientists begun to understand its extraordinary biological significance. Unlike many dietary antioxidants, ergothioneine behaves more like a cell-protective micronutrient—one that the human body actively absorbs, transports, and stores in tissues prone to degeneration, inflammation, and oxidative stress. This unique behavior has led many researchers to consider ergothioneine a potential “missing essential nutrient” for human health.
Ergothioneine is naturally produced only by fungi and certain bacteria, which means humans must obtain it from diet or supplementation. Once ingested, it is transported through a specialized transporter known as OCTN1 (Ergothioneine Transporter). The existence of this dedicated transport system suggests that ergothioneine serves biological functions more important than previously recognized, with potential implications for cognitive health, immune regulation, metabolic balance, and healthy aging.
1. What Is Ergothioneine? Understanding Its Unique Nature
Ergothioneine is a naturally occurring amino acid derivative formed from histidine, but what makes it distinguished from common amino acids is its unusual sulfur-containing molecular structure. This structure gives it exceptional stability, resistance to oxidation, and the ability to withstand harsh biological environments that would break down other antioxidants.
While antioxidants such as vitamin C or glutathione play well-known roles in neutralizing free radicals, they are relatively short-lived and require constant replenishment. Ergothioneine, however, is different—it remains stable for long periods, accumulates in key tissues, and performs protective functions without becoming pro-oxidant even at higher concentrations. This uncommon behavior is one of the main reasons researchers believe it may act as a long-term protectant against cellular damage.
2. How Ergothioneine Works in the Human Body
Ergothioneine does far more than simply act as an antioxidant. Its biological effects extend into cellular energy production, inflammation control, mitochondrial preservation, and long-term tissue resilience. Below is how the human body uses it:
2.1 A Powerful Defense Against Oxidative Damage
Oxidative stress is a constant threat to human cells. It occurs when metabolic activity, environmental toxins, UV exposure, poor diet, or stress lead to an excess of reactive oxygen species that damage DNA, proteins, and lipids. Over time, this contributes to aging, chronic inflammation, and deterioration of organ function.
Ergothioneine plays a sophisticated role in preventing oxidative injury. It distributes itself to areas where oxidative damage is most likely to occur—such as the mitochondria, red blood cells, bone marrow, the liver, and the brain—and neutralizes unstable reactive molecules before they disrupt cellular processes. Beyond quenching free radicals, it helps stabilize the entire internal redox environment of the cell, maintaining biochemical balance even under stress. This stabilizing action is especially important in tissues with high energy demands and limited antioxidant defenses.
2.2 Protecting Mitochondria and Sustaining Cellular Energy
Mitochondria, often described as the energy engines of cells, are both essential and vulnerable. They generate ATP through oxidative reactions, but this very process also produces highly reactive molecules that can damage mitochondrial DNA and impair energy output.
Ergothioneine has demonstrated a strong affinity for mitochondrial tissues, where it accumulates to support energy production and minimize oxidative wear. By preserving mitochondrial integrity, ergothioneine helps maintain stable ATP levels, prevents the decline of metabolic efficiency, and supports the cellular recovery process after stress. This is particularly relevant for aging, fatigue, athletic performance, and chronic inflammatory conditions where mitochondria are under sustained pressure.
2.3 Modulating Inflammation and Immune Response
Inflammation is essential for healing, but chronic inflammation accelerates tissue aging and increases the risk of numerous diseases. Ergothioneine interacts with immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils, helping them function effectively without triggering unnecessary inflammatory cascades.
Studies indicate that ergothioneine decreases the production of inflammatory signaling molecules and protects immune cells from the oxidative bursts they generate during immune defense. This dual action—protective and regulating—positions ergothioneine as a valuable compound for long-term inflammatory balance.
2.4 Supporting Brain Health and Cognitive Function
The brain consumes significant energy and oxygen, making it highly vulnerable to oxidative and inflammatory stress. Ergothioneine is transported into the brain through OCTN1 receptors, with high concentrations detected in regions vital for memory, learning, and emotional stability.
Research suggests that ergothioneine may help:
-
Preserve neuronal mitochondria
-
Protect brain tissues from oxidative and inflammatory damage
-
Maintain cognitive clarity during aging
-
Reduce the risk associated with neurodegenerative decline
Observational studies in older adults have shown that individuals with lower ergothioneine levels tend to exhibit greater signs of frailty and cognitive impairment, suggesting a potential protective role.
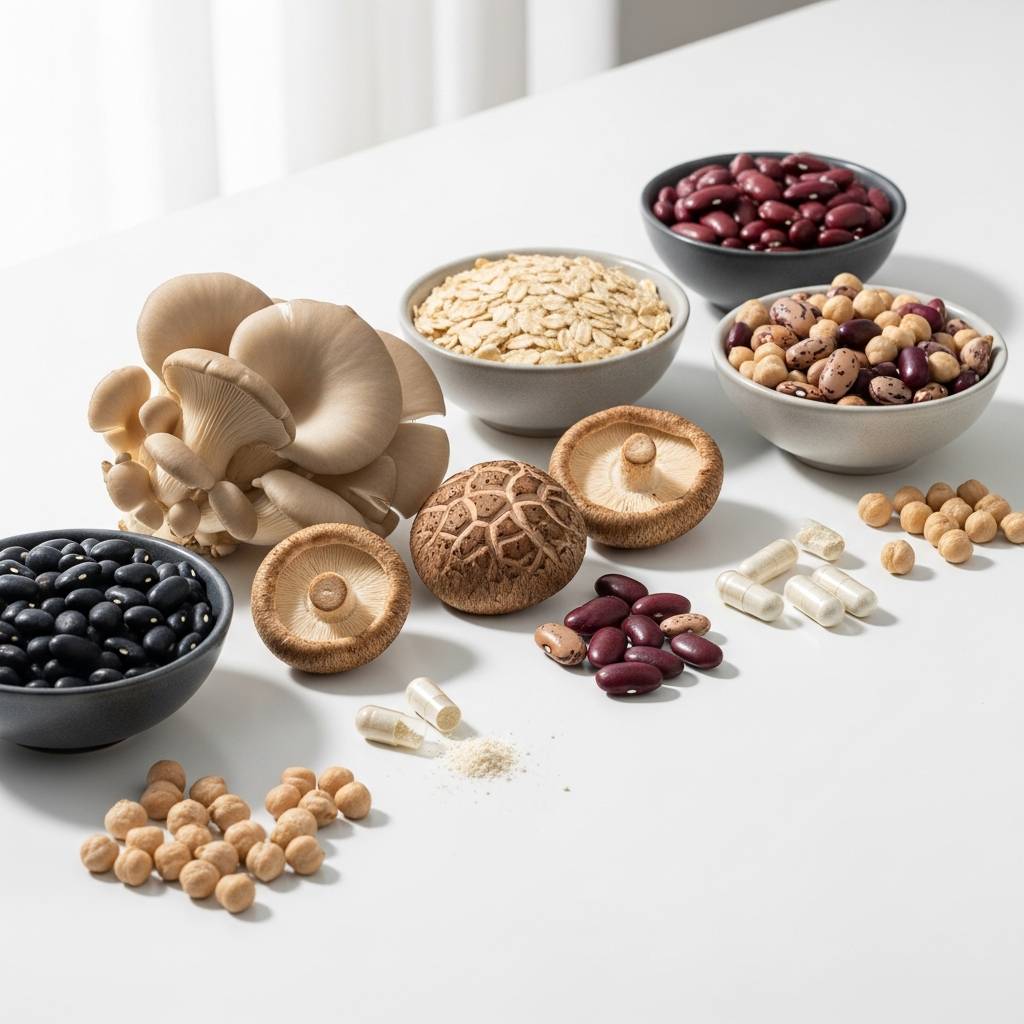
3. Natural Sources of Ergothioneine
Humans cannot produce ergothioneine, but can obtain it from certain foods. The richest dietary sources come from fungi:
Highest Sources
-
Oyster mushrooms
-
Shiitake, maitake, king trumpet mushrooms
-
Porcini mushrooms
Moderate Sources
-
Black beans and kidney beans
-
Oats
-
Garlic
-
Organ meats (from animals that consumed ergothioneine-rich foods)
Even so, average daily intake from diet is extremely low. Modern diets, which lack mushroom diversity, often fail to reach potentially beneficial levels—another reason supplementation has become popular in functional nutrition and longevity-focused formulations.
4. Scientific Research and Health Benefits of Ergothioneine
Ergothioneine stands out among longevity-related nutrients because its effects have been observed across multiple organ systems. A growing body of research suggests that maintaining sufficient ergothioneine levels may contribute to healthier aging and protection against chronic diseases. The following sections summarize the most notable areas of scientific interest.
4.1 Cognitive Health and Neuroprotection
The brain is particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress due to its high oxygen consumption and dense network of mitochondria. Ergothioneine accumulates selectively in brain regions responsible for memory, learning, and emotional regulation—an effect made possible by the OCTN1 transporter expressed in neural tissues.
How It Supports the Brain
Ergothioneine provides broad protection by:
-
Shielding neuronal mitochondria from oxidative overload
-
Supporting glutathione activity in neural cells
-
Reducing microglial-driven inflammation
-
Preserving membrane integrity and synaptic function
In human observational studies, individuals with lower circulating ergothioneine levels showed higher rates of cognitive decline and frailty. While more clinical research is needed, the consistent association between low ergothioneine levels and cognitive impairment has sparked interest in using ergothioneine as a tool for brain aging support.
4.2 Cardiovascular and Endothelial Support
The cardiovascular system endures constant mechanical and oxidative stress. Vascular endothelial cells, in particular, are sensitive to free radical exposure that can lead to dysfunction, arterial stiffness, and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
Ergothioneine influences cardiovascular health through several pathways:
-
Protecting endothelial cells from oxidative injury
-
Reducing lipid peroxidation, including oxidation of LDL cholesterol
-
Supporting nitric oxide signaling, which benefits vascular elasticity
-
Reducing inflammatory cytokines involved in vascular damage
Preclinical findings suggest that ergothioneine may contribute to long-term cardiovascular resilience, especially in populations with elevated oxidative or metabolic stress.
4.3 Immune Modulation and Inflammatory Balance
The immune system generates bursts of reactive molecules to neutralize pathogens. However, excessive or poorly regulated immune responses contribute to chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
Ergothioneine’s effect on the immune system is twofold:
-
Protecting immune cells from self-generated oxidative bursts
-
Regulating inflammatory signaling to prevent chronic overactivation
This dual role supports immune efficiency while protecting tissues from inflammatory wear. Growing evidence supports its contribution to immune resilience in aging populations.
4.4 Metabolic and Mitochondrial Health
Mitochondria produce energy through oxidative processes that inherently create reactive byproducts. When mitochondrial defenses fail, cells experience fatigue, metabolic inefficiency, and accelerated aging.
Ergothioneine’s presence inside mitochondria allows it to:
-
Protect mitochondrial DNA
-
Maintain respiratory chain function
-
Support ATP production under stress
-
Reduce mitochondrial inflammation
Because mitochondrial decline is linked to fatigue, metabolic slowdown, and neurodegeneration, ergothioneine’s role in sustaining mitochondrial activity is considered a key aspect of its longevity-supporting potential.
4.5 Muscle Recovery and Physical Performance
Exercise produces high levels of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle. While antioxidants can be beneficial, some antioxidant supplements interfere with beneficial exercise adaptations. Ergothioneine does not exhibit this downside.
Instead, it supports muscle performance by:
-
Reducing exercise-induced oxidative stress
-
Supporting mitochondrial efficiency during exertion
-
Enhancing recovery time
-
Protecting muscle fibers from long-term wear
These attributes make ergothioneine a promising ingredient for athletic and recovery formulations.
4.6 Liver Health and Detoxification Pathways
The liver is exposed to high levels of metabolic stress and toxic byproducts. Ergothioneine accumulates strongly in liver tissues and may contribute to:
-
Protection against oxidative liver injury
-
Reduced lipid peroxidation in metabolic dysfunction
-
Enhanced phase II detoxification processes
-
Better tolerance to chemical and environmental stressors
As interest grows in liver-support supplements, ergothioneine is being studied for potential use alongside milk thistle, NAC, and glutathione.
4.7 Skin Health, UV Defense, and Anti-Aging Effects
Skin cells are consistently exposed to UV radiation and environmental pollutants. Ergothioneine’s stability under UV exposure makes it particularly valuable in both oral and topical formulations.
Documented benefits include:
-
Reduced UV-induced free radical formation
-
Support for fibroblast mitochondrial energy
-
Protection of collagen-producing cells
-
Improved hydration and elasticity
-
Enhanced recovery from environmental stress
Because of these characteristics, ergothioneine is increasingly included in beauty-from-within supplements, nutricosmetics, and premium anti-aging skincare.
5. Ergothioneine Supplementation: Absorption, Dosage, and Forms
5.1 Absorption and Bioavailability
Ergothioneine is absorbed directly through the OCTN1 transport system, which makes its bioavailability markedly higher than many common antioxidants. Once absorbed, it is selectively transported to organs where oxidative stress is most threatening—such as the liver, brain, bone marrow, and reproductive tissues.
This targeted transport gives ergothioneine a biological efficiency unmatched by many other antioxidant nutrients.
5.2 Recommended Dosage
There is no universally established “official” dosage because ergothioneine is not yet classified as a vitamin. However, research and commercial supplement use commonly range between:
-
5–30 mg per day for general antioxidant support
-
30–50 mg per day for cognitive, cardiovascular, or anti-aging support
-
100 mg+ occasionally used in clinical research without safety concerns
Its long half-life means daily supplementation gradually increases tissue levels.
5.3 Supplement Forms
Ergothioneine is available in several formats:
-
Capsules or tablets(most common, stable absorption)
-
Powder blends(Commonly used in energy formulas and antioxidant combinations)
-
Functional beverages(High-stability raw materials required)
-
Topical serums/creams(for anti-aging skin care)
Most high-quality supplements use pure L-ergothioneine, the bioactive form utilized by the body.
6. Safety, Tolerability, and Suitable Populations
Ergothioneine has one of the most favorable safety profiles among antioxidant nutrients. Studies—including long-term toxicity tests—show:
-
No adverse effects at high doses
-
No organ toxicity
-
No pro-oxidant behavior
-
Excellent long-term tolerability
Suitable For:
-
Individuals concerned with cognitive aging
-
Adults under oxidative or metabolic stress
-
Athletes requiring mitochondrial support
-
People exposed to pollution, UV, or lifestyle stress
-
Healthy aging and longevity-focused consumers
Precautionary Situations:
-
Pregnancy and breastfeeding(Limited data)
-
Individuals on immune-suppressing therapy(need to consult a doctor)
Overall, ergothioneine demonstrates exceptional safety for general adult use.
7. Market Trends: Why Global Brands Are Turning to Ergothioneine
Ergothioneine is emerging as a premium ingredient in:
-
Longevity formulations
-
Brain health supplements
-
Anti-aging skincare
-
Energy and mitochondrial support blends
-
Immunity-focused products
-
Mushrooms and adaptogenic blends
Three major reasons drive its rapid adoption:
1. Strong scientific foundation
Over 100+ published studies highlight its protective effects.
2. Unique biological transport system
Few nutrients have a dedicated transporter—this gives ergothioneine an advantage.
3. Consumer interest in longevity ingredients
With rising demand for healthy aging solutions, ergothioneine aligns perfectly with modern wellness trends.
8. Ergothioneine Supplement Manufacturing: Why Quality Matters
Because ergothioneine is a sensitive amino acid with unique transport and stability characteristics, manufacturing high-quality ergothioneine supplements requires strict control over raw material purity, moisture levels, encapsulation environment, and dosage accuracy. Not all manufacturers have the technical expertise or production conditions necessary to handle advanced longevity ingredients.
This has led many global brands—especially those developing brain health, longevity, and antioxidant-led formulations—to partner with specialized manufacturers capable of GMP-level precision and international export standards.
8.1 Example of a Professional Ergothioneine Manufacturer in China
China has rapidly grown into a global hub for innovative supplement manufacturing, particularly in functional ingredients such as ergothioneine, NMN, L-theanine, and mushroom-based products. One of the manufacturers contributing to this development is ZOOMSHEAL Health, a contract manufacturer supplying custom formulations to brands in the United States, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia.
Why ZOOMSHEAL is relevant in this category
ZOOMSHEAL specializes in producing high-stability antioxidant supplements—including ergothioneine—across different dosage forms such as:
-
Capsules(HPMC / gelatin options)
-
Powders and blends
-
Functional beverages
-
Effervescent and chewable formats
-
Beauty-from-within formulations combining ergothioneine with collagen, hyaluronic acid, or antioxidants
To ensure ergothioneine remains potent through its entire shelf life, ZOOMSHEAL applies:
-
Low-humidity encapsulation systems
-
Precision micro-dosing for antioxidant ingredients
-
Third-party testing for purity and assay
-
Advanced packaging options, including moisture-resistant bottles and nitrogen flushing
-
GMP, ISO, HACCP, Halal certifications for global compliance
These capabilities allow brands to create stable, high-quality ergothioneine products that maintain their bioactivity even under long transport routes or challenging climates.
8.2 Custom Formulation Opportunities with Ergothioneine
Brands looking to differentiate in the competitive longevity market increasingly request custom ergothioneine blends. ZOOMSHEAL supports product development by combining ergothioneine with synergistic ingredients such as:
-
L-glutathione (enhance antioxidant synergy)
-
CoQ10 + PQQ( (can support combination)
-
Lion's Mane or mushroom complex (consistent with natural sources)
-
L-theanine (suitable for decompression + brain health)
-
Collagen / Astaxanthin(beauty anti-aging)
These combinations align with current market trends toward multi-functional, science-backed longevity formulas.
8.3 Why Global Brands Choose Chinese Manufacturers for Ergothioneine
Companies like ZOOMSHEAL are becoming preferred partners for global brands because: Chinese manufacturers in:
- Raw material procurement chain (especially mushroom extraction and fermentation raw materials)
- Cost optimization capabilities (suitable for brands to expand production)
- OEM/ODM flexibility
- Rapid development cycle
- Complete international certifications
has strong advantages.
As ergothioneine becomes a more prominent ingredient in longevity and brain-health formulations, manufacturers with the ability to maintain ingredient stability and offer custom development solutions are particularly valuable.
Ergothioneine represents a new frontier in cellular health, offering a broad spectrum of protection that extends far beyond traditional antioxidants. Its ability to safeguard mitochondria, reduce inflammation, support cognitive longevity, and enhance resilience across vital organs makes it an exceptional compound for modern wellness. As scientific interest continues to grow, ergothioneine is expected to become a foundational ingredient in advanced nutritional formulations.
Ergothioneine — Reference List (APA Style)
1. Cheah, I. K., Tang, R. M. Y., Yew, T. S. Z., & Halliwell, B. (2023).
Ergothioneine: An under-recognised dietary micronutrient required for healthy ageing?
Antioxidants, 12(1).
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9816654/
2. Musci, I., & Bonaccorsi, G. (2022).
Ergothioneine as a natural antioxidant against oxidative stress-related diseases.
Nutrients, 14(7).
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35370675/
3. Zhu, Y. J., Chen, L., & Kong, L. (2022).
Ergothioneine: A stress vitamin with anti-aging, vascular, and neuroprotective potential.
Frontiers in Pharmacology, 13.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9221166/
4. Yan, Y., Zhang, Z., & Wu, J. (2024).
Ergothioneine and its congeners: Anti-ageing mechanisms and biological roles.
Protein & Cell, 15(3), 191–205.
https://academic.oup.com/proteincell/article/15/3/191/7240455
5. Cheah, I. K., & Halliwell, B. (2020).
The biology of ergothioneine, an antioxidant nutraceutical.
Frontiers in Pharmacology, 11.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7653990/
6. Xia, D., Li, D., & Wang, R. (2024).
Ergothioneine promotes longevity and healthy aging in male mice.
Aging Cell, 23(4).
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11226696/
7. Li, X., Sun, H., & Jiang, C. (2024).
Ergothioneine and mitochondria: An important protective role under oxidative stress.
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 670, 68–74.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006291X24008052
8. Cheah, I. K., Tang, R. M. Y., & Halliwell, B. (2017).
Ergothioneine – A mitochondrial antioxidant?
Journal of Integrative Medicine, 15(5), 293–298.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095496417300802
9. Halliwell, B., & Gutteridge, J. M. (2015).
Free radicals in biology and medicine. (Foundational background reference on oxidative stress mechanisms.)